Seznamy 32 Quantum Mechanical Model Of Hydrogen Atom
Seznamy 32 Quantum Mechanical Model Of Hydrogen Atom. • what does it do? The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the …
Tady The Quantum Mechanical Model Of The Atom Article Khan Academy
This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. • when do we need it? The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics? From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct.We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the.
The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Show activity on this post. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave.

We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).. N= 1, 2, 3, etc... Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

N= 1, 2, 3, etc. . Grit your teeth and bear it.

Show activity on this post. • how does it apply to the h atom? Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. • when do we need it? We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. Show activity on this post. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. What should we use as a test? Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms.

• how does it apply to the h atom? The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. • what does it do? Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. . What should we use as a test?

Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was... • what does it do? • how does it apply to the h atom? The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics.

Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. • when do we need it? We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. N= 1, 2, 3, etc. • when do we need it? • how does it apply to the h atom? The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics? Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

Show activity on this post. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. What should we use as a test?.. How about the simplest system that we can think of.
Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics?. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. Grit your teeth and bear it... • how does it apply to the h atom?

*the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave... The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. N= 1, 2, 3, etc. • what does it do? From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct.. Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics.

N= 1, 2, 3, etc. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. How about the simplest system that we can think of. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math.. • when do we need it?
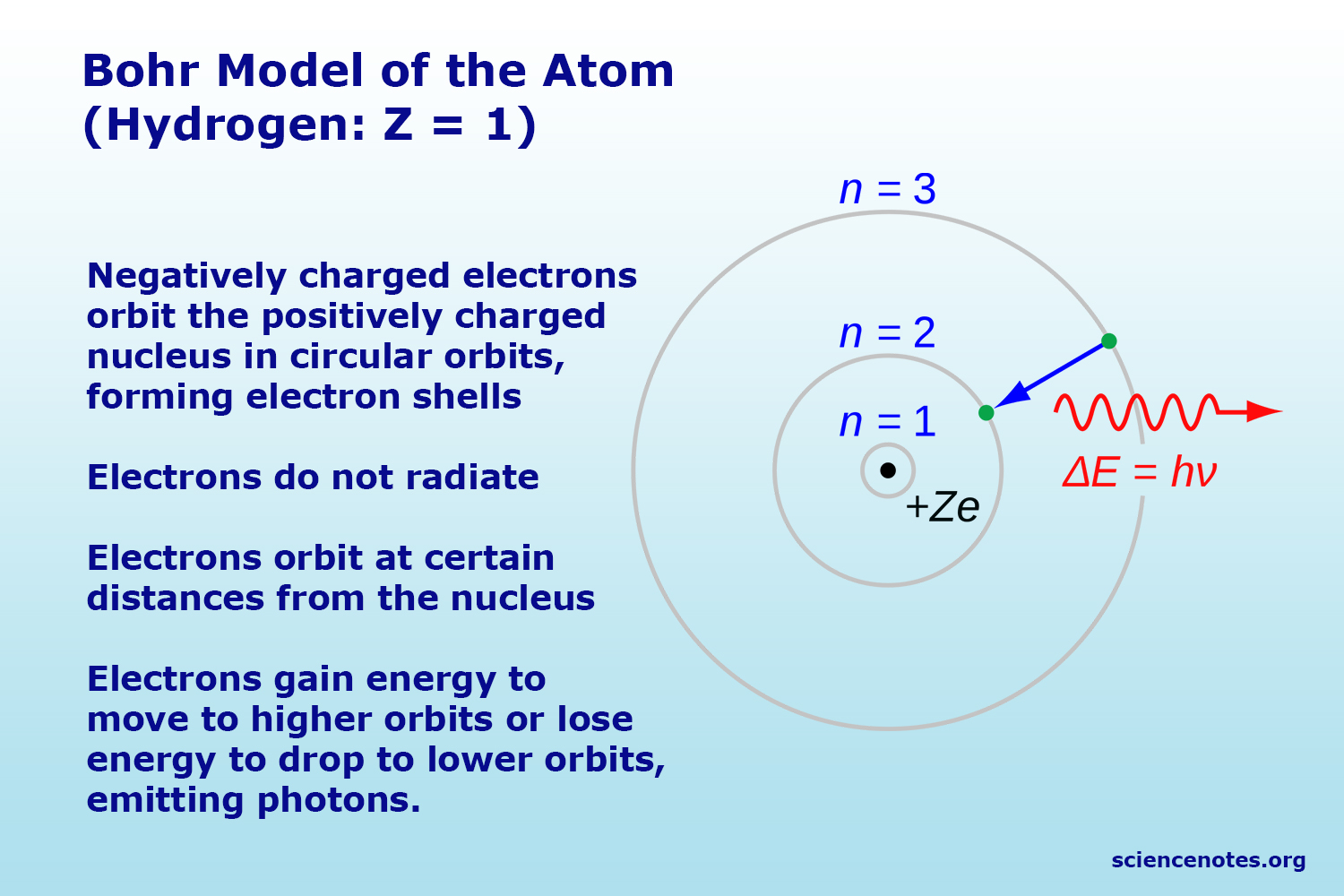
The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms.. • how does it apply to the h atom?.. Show activity on this post.
N= 1, 2, 3, etc. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. Grit your teeth and bear it. What should we use as a test? From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. • what does it do? Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics? The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

Grit your teeth and bear it. • when do we need it? The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom.. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the …

• when do we need it? We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Show activity on this post. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. • what does it do? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math.

The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct.. Show activity on this post.

Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math... Show activity on this post. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. • what does it do? • when do we need it? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … • how does it apply to the h atom? Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).. What should we use as a test?

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.. What should we use as a test? The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … How about the simplest system that we can think of. Grit your teeth and bear it. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. • how does it apply to the h atom? Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. How about the simplest system that we can think of.

The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the.

What should we use as a test?.. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. • how does it apply to the h atom? Show activity on this post. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).. Grit your teeth and bear it.

*the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave... • how does it apply to the h atom? N= 1, 2, 3, etc. What should we use as a test? Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. Grit your teeth and bear it. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

Show activity on this post. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. Grit your teeth and bear it. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the …

Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom... • how does it apply to the h atom? N= 1, 2, 3, etc. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom.

Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. • how does it apply to the h atom? Grit your teeth and bear it. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.
The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms.. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. • when do we need it?. N= 1, 2, 3, etc.

The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number.. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. • what does it do? What should we use as a test? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics?

The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms... We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.

Show activity on this post. N= 1, 2, 3, etc. • when do we need it? Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. How about the simplest system that we can think of. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy... We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).

*the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave.. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. N= 1, 2, 3, etc. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. • when do we need it? Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. • how does it apply to the h atom?

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation... Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. Grit your teeth and bear it.

How about the simplest system that we can think of. . Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

What should we use as a test?.. .. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.

What should we use as a test? From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. • how does it apply to the h atom?. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located).

The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. How about the simplest system that we can think of. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation... The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy.

Grit your teeth and bear it. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. How about the simplest system that we can think of.

Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. N= 1, 2, 3, etc.. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number.. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Show activity on this post... The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. • how does it apply to the h atom? What should we use as a test? The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics.. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

• how does it apply to the h atom?. What should we use as a test? Show activity on this post... Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

How about the simplest system that we can think of. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. How about the simplest system that we can think of. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. • how does it apply to the h atom? Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something.

Grit your teeth and bear it. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). Grit your teeth and bear it. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. How about the simplest system that we can think of... The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model.

How about the simplest system that we can think of. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. N= 1, 2, 3, etc. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. Now that we have discovered a new theory (quantum mechanics as exemplified by schrödinger's equation) we ought to test it out on something. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number... We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the.

• how does it apply to the h atom? The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. • how does it apply to the h atom? Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics? The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.. *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave.
The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model. We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. N= 1, 2, 3, etc.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Show activity on this post. What should we use as a test? • when do we need it? Grit your teeth and bear it. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics... The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom.

The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom.. • what does it do? Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 quantum mechanics (qm) quantum mechanics is… • the set of rules obeyed by small systems (molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles) • one of the two greatest achievements of 20th century physics. Grit your teeth and bear it.. Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics.

The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. What should we use as a test? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Quantum theory of the hydrogen atom 6.1 schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen atom today's lecture will be all math. From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. Grit your teeth and bear it. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The first feature relates to the particular nature of the coulomb potential energy. Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

The hydrogen atom in this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the … • what does it do? • when do we need it? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Solution of the dirac equation for hydrogen the standard hydrogen atom problem can be solved exactly using relativistic quantum mechanics. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. The principal quantum number, the azimuthal quantum number, the magnetic quantum number, and the spin quantum number. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model.. Chem 1310 a/b fall 2006 questions • what is quantum mechanics?

*the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The introduction of stationary states to atomic physics was bohr's main contribution to the quantum theory of atoms. • what does it do? From these functions, taken as a complete basis, we will be able to construct. What should we use as a test? *the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave.. The issue with classical physics understanding of the mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is explaining how orbiting electrons do not lose energy and spiral into the …

• how does it apply to the h atom? N= 1, 2, 3, etc. • when do we need it?. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.

*the quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. Grit your teeth and bear it. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. • when do we need it? We note that the potential energy depends only on the distance from the origin (where the proton is located). We have already seen that (even with no applied fields), while the total angular momentum operator commutes with the dirac hamiltonian, neither the. The hydrogen atom 12th april 2008 i. The set of orbitals belonging to a given principal quantum number n constitutes what we call a shell in the orbital model... The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.